There is software named as GEOGEBRA. It is a free, open –source,
and multi-platform software that combines dynamic geometry, algebra, calculus,
spreadsheet, graphing and statistics in one easy-to-use package. Let us start
learning this software. Geogebra was created by Markus Hohenwater in 2001/2002
as a part of his Masters and PhD project in mathematics education at the
University of Salzburg in Austria. During that time, geogebra won several
international awards, including the European and German educational software
awards. Since 2006 geogebra is supported by the Austrian Ministry of Education
to maintain the free availability of the software for mathematics education at
schools and universities. We will use the latest version of geogebra ( i.e.
4.2)
After you install the geogebra software
-
This icon appears on
the desktop. Double clicking this icon the following geogebra window appears. There are six main parts of geogebra window.
They are as follows: (1) Title bar (2) Menu
bar (3) Tool bar (4) Algebra view (5) Graphics view (6) Input bar .
 |
| GeoGebra |
Now we will move towards the tools
that are present in the tool bar. The tool bar is divided in twelve toolboxes.
They are as follows: (1)Move (2) New
point (3) Line trough two points (4) Perpendicular line (5) Polygon (6) Circle with centre
through point (7) Ellipse (8) Angle (9) Reflect object about line (10) Insert text (11) Slider (12) Move graphics view
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12.
These
toolboxes contain various tools which fall in the same category as per the main
toolbox. They are as follows:
(1).Move:
This toolbox contains three tools in all. They are –
- Move
,
Rotate around point
, Record to the spreadsheet.
- Move
Rotate around point
(2).New point:
This toolbox contains six tools in all. They are -
- New point
,
-Point on object
,
-Attach/detach point
,
- Intersect two object
,
- Midpoint or center
,
- Complex number
.
- New point
-Point on object
-Attach/detach point
- Intersect two object
- Midpoint or center
- Complex number
(3).
Line through
two points: This toolbox contains seven tools in all. They are -
- Line through two points
,
- Segment between two points
,
- Segment with fixed length
,
-Ray between two points
,
-Polyline between points
,
-Vector between two points
,
-Vector from point
.
- Line through two points
- Segment between two points
- Segment with fixed length
-Ray between two points
-Polyline between points
-Vector between two points
-Vector from point
(4).
Perpendicular
line: This toolbox contains eight tools in all. They are –
-Perpendicular line
,
- Parallel line
,
- Perpendicular bisector
,
- Angle bisector
,
- Tangents
,
- Polar or diameter line
,
- Best fit line
,
- Locus
.
-Perpendicular line
- Parallel line
- Perpendicular bisector
- Angle bisector
- Tangents
- Polar or diameter line
- Best fit line
- Locus
(5).
Polygon:
this toolbox contains four tools in all. They are –
- Polygon
,
- Regular polygon ,
- Rigid polygon
,
- Vector polygon
.
- Polygon
- Regular polygon
- Rigid polygon
- Vector polygon
(6).
Circle with
centre through point: This toolbox contains nine tools in all.
They are -
- Circle with centre through point
,
- Circle with centre and radius
,
- Compass
,
- Circle through three points
,
- Semicircle trough two points
,
- Circular arc with centre between two points
,
- semicircular arc through three points
,
- Circular sector with centre between two points
,
- circumcircular sector through three points
.
- Circle with centre through point
- Circle with centre and radius
- Compass
- Circle through three points
- Semicircle trough two points
- Circular arc with centre between two points
- semicircular arc through three points
- Circular sector with centre between two points
- circumcircular sector through three points
(7).
Ellipse:
This toolbox contains four tools in all. They are –
- Ellipse
,
- Parabola
,
- Hyperbola
,
- Conic through five points
.
- Ellipse
- Parabola
- Hyperbola
- Conic through five points
(8).
Angle:
This toolbox contains six tools in all. They are –
- Angle
,
- Angle with given size
,
- distance or length
,
- Area
,
- Slope
,
- Create list
.
- Angle with given size
- distance or length
- Area
- Slope
- Create list
(9).
Reflect
object about line: This toolbox contains six tools in all. They
are –
- Reflect object about line
,
- Reflect object about point
,
- Reflect object about circle
,
- Rotate object around point by angle
,
- Translate object by vector
,
- dialect object from point by factor
.
- Reflect object about line
- Reflect object about point
- Reflect object about circle
- Rotate object around point by angle
- Translate object by vector
- dialect object from point by factor
(10).
Insert text:
This toolbox contains seven tools in all. They are –
- Insert text
,
- Insert image
,
- Pen
,
- Freehand shape
,
- Relation between two objects
,
- Probablity calculator
,
- Function inspector
.
(11). Slider: This toolbox contains four tools in all. They are –
- Slider
,
- Check box to show/hide objects
,
- Insert button
,
- Insert input box
.
- Insert text
- Insert image
- Pen
- Freehand shape
- Relation between two objects
- Probablity calculator
- Function inspector
(11). Slider: This toolbox contains four tools in all. They are –
- Slider
- Check box to show/hide objects
- Insert button
- Insert input box
(12).
Move graphics
view: This toolbox contains seven tools in all. They are –
- Move graphics view
,
- Zoom in
,
- Zoom out
,
- Show/hide object
,
- Show/hide label
,
- Copy visual style
,
- Delete object
.
NOTE: The uses and how to use these tools you will come to know when you point your cursor on these tool buttons that are shown in the picture.
- Move graphics view
- Zoom in
- Zoom out
- Show/hide object
- Show/hide label
- Copy visual style
- Delete object
NOTE: The uses and how to use these tools you will come to know when you point your cursor on these tool buttons that are shown in the picture.
Let
us see one example:-
Question: Construct a regular polygon with six sides using
the ‘polygon’ tool.
Solution: (1) select the Circle with
Centre through point tool.(1)
In the Graphics view, click at a point A and
another suitable point B to draw a circle c with centre A
through point B.(2)
Similarly, draw a circle d through with centre B
through point A.(3)
Intersect the circles c and d with the Intersect Two Objects
tool to get the hexagon’s vertices C and D.(4)
Draw circle e with centre C through point A
and circle f
with centre D
through point A.(5)
Select the New Point tool and click at the intersection
of the circles c
and e
to get the vertex e to get the vertex E, and at the intersection of
the circles c
and f
to get the vertex F.(6)
Draw circle g with centre F through point A.(7)
Using the New Point tool, click at the intersection of
the circles c
and g
to get the vertex G.(8)
Select the Polygon tool, and click on the vertices, other
than A
in sequence till you get a closed polygon. The graphics view shows the regular
six-sided polygon (i.e., regular hexagon)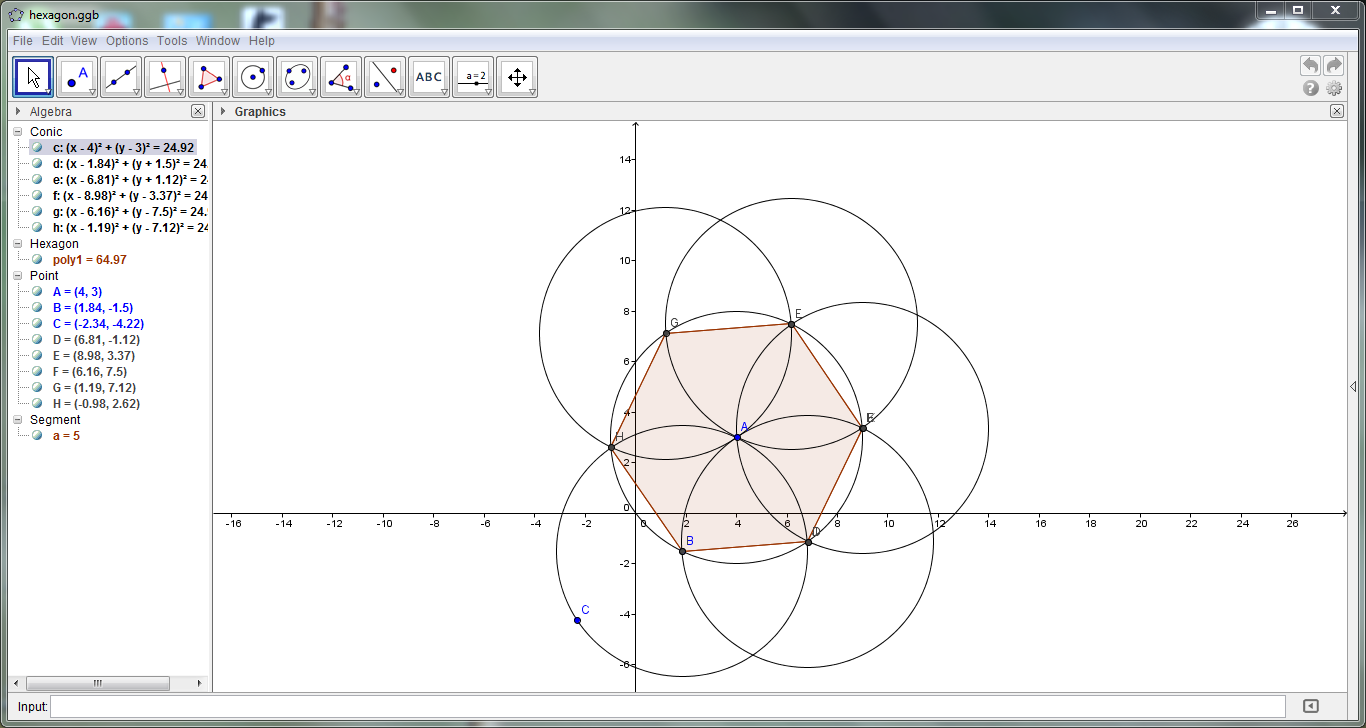
To download GeoGebra :
1. Go to GeoGebra.org OR
2. Click on the links below -

To download GeoGebra :
1. Go to GeoGebra.org OR
2. Click on the links below -
Do SUBCRIBE to GETin by entering your email on the top right corner.
Do And don't forget to follow GETin on Google+.








































































No comments:
Post a Comment